An overview of IoT and its definition:
IoT, or the Internet of Things, refers to the interconnected network of physical devices, vehicles, buildings, and other items that are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies, allowing them to collect and exchange data over the internet. The goal of IoT is to create intelligent, connected systems that can collect and analyze data, enabling the automation of various tasks and making it possible to make data-driven decisions.
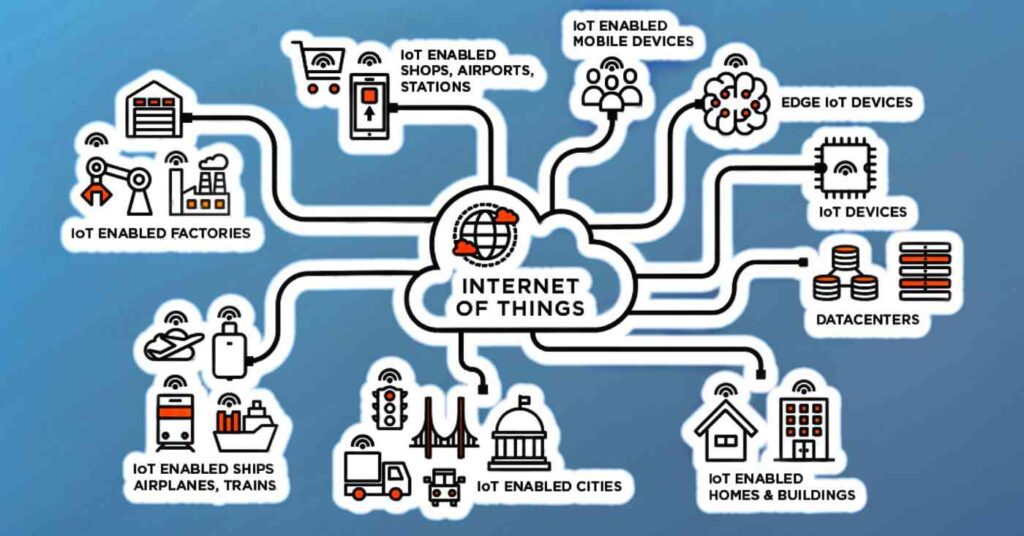
IoT use cases and real-world examples in various industries:
IoT is being used in a wide variety of industries to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and gain new insights into how products and services are being used. Some examples include:
- Manufacturing: IoT sensors can be used to monitor the performance of machines, identify potential issues, and schedule maintenance before a problem occurs.
- Healthcare: IoT devices such as wearables and remote monitoring systems are being used to track patients’ vital signs and send the data to healthcare professionals for analysis.
- Transportation: IoT technology is being used in connected cars and public transportation systems to improve traffic flow and reduce accidents.
- Agriculture: IoT sensors are being used to monitor crop growth and optimize irrigation systems.
- Smart cities: IoT sensors and cameras are being used to monitor traffic, air quality, and energy usage in order to improve the quality of life for citizens.
The benefits of IoT:
IoT can offer a wide range of benefits, including improved efficiency, cost savings, and new insights into how devices are being used. By collecting and analyzing data, businesses can make data-driven decisions, improve efficiency, and gain new insights into their products and services. IoT can also lead to new revenue streams and improved customer engagement.
The challenges and limitations of IoT:
The Internet of Things (IoT) has the potential to bring many benefits to individuals, businesses, and society as a whole. Some of the key benefits of IoT include:
- Increased Efficiency: IoT devices can automate processes and gather data that can be used to improve efficiency and reduce costs. For example, smart factories can use IoT sensors to monitor production in real-time, allowing for quick adjustments to improve efficiency.
- Improved Quality of Life: IoT devices can be used to improve the quality of life for individuals in a variety of ways. For example, smart home systems can be used to control lighting, temperature, and security remotely, making it easier for people to manage their homes.
- Better Decision Making: IoT devices can gather vast amounts of data that can be used to make more informed decisions. For example, cities can use IoT devices to collect data on traffic patterns and air quality, which can be used to improve transportation and urban planning.
- Enhanced Safety and Security: IoT devices can be used to enhance safety and security in a variety of settings. For example, IoT sensors can be used to monitor industrial equipment for signs of wear and tear, reducing the risk of accidents.
- Increased Connectivity: IoT devices can increase connectivity between people, processes, and data, which can lead to new opportunities for innovation and growth.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: IoT devices allow for remote monitoring and control of systems and devices. This enables businesses and organizations to keep track of their operations and assets even when they are not on site.
- Predictive Maintenance: IoT devices can gather data and use it to predict when equipment is likely to fail, allowing for preventative maintenance to be carried out before the failure occurs.
Overall, IoT has the potential to bring many benefits and improvements in various fields, from healthcare, transportation, manufacturing, home automation, and many more.
The future of IoT and emerging trends:
IoT is a rapidly growing field, and new technologies and trends are emerging all the time. Some of the key trends to watch in the future of IoT include:
- 5G: 5G networks will enable faster and more reliable connectivity for IoT devices, making it possible to handle the huge amounts of data generated by IoT.
- Edge computing: Edge computing allows data to be processed closer to where it is generated, reducing latency and making it possible to handle large amounts of data in real-time.
- Artificial intelligence: AI can be used to analyze the data generated by IoT devices, making it possible to gain new insights and automate tasks.
The role of IoT in Industry 4.0 and the fourth industrial revolution:
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a crucial enabler of Industry 4.0 and the fourth industrial revolution. Industry 4.0 refers to the integration of advanced technologies, such as IoT, AI, and big data, into manufacturing and other industries. IoT allows for the seamless integration of data and connectivity between devices, machines, and systems, which can be used to improve efficiency and optimize performance. IoT devices can also improve maintenance, safety, and the integration of advanced technologies such as AI and big data. Overall, IoT is helping to transform the way we live and work and make the industry more efficient and sustainable.
The impact of IoT on society, economy and environment:
IoT has the potential to improve people’s lives, create new job opportunities, and drive economic growth. However, it can also have negative impacts on the environment and society if not used responsibly. For example, the increased use of IoT devices can lead to an increase in electronic waste and energy consumption.
The role of IoT in Smart Home and building automation:
IoT devices and technologies are being used in homes and buildings to automate various tasks and improve energy efficiency. For example, IoT devices can be used to control lighting, heating, and cooling systems and monitor energy usage.
The role of IoT in the connected car and transportation:
IoT technology is being used in connected cars and transportation systems to improve traffic flow, reduce accidents and enhance the overall transportation experience.
IoT and its role in the Internet of Everything (IoE) and the potential integration with other technologies:
IoT is a key component of the Internet of Everything (IoE), which refers to the interconnected network of people, processes, data, and things. The integration of IoT with other technologies such as blockchain and quantum computing can enhance the capabilities of IoT and enable new applications. For example, blockchain can be used to secure the data transmitted by IoT devices and quantum computing can be used to analyze vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Internet of Things (IoT) is a rapidly growing field that has the potential to revolutionize a wide range of industries and improve people’s lives. However, it is important to be aware of the challenges and limitations of IoT and to use this technology responsibly. The integration of IoT with other technologies such as blockchain and quantum computing can enhance its capabilities and enable new applications. The future of IoT is exciting, and it will be interesting to see how it continues to evolve and impact our world. With IoT, we are headed towards a more connected, intelligent and automated future, and we are just scratching the surface of what is possible.

























